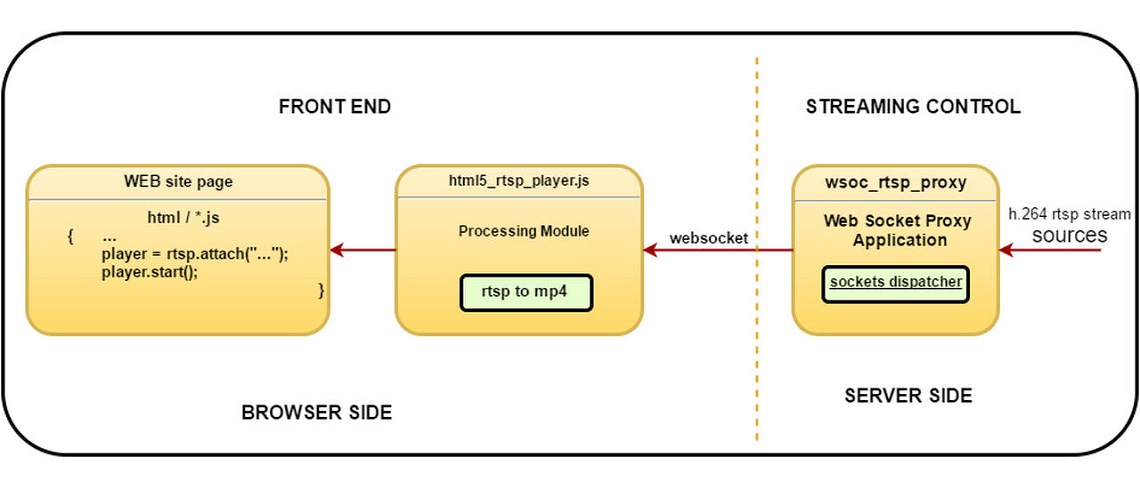
Attach HTML Video with RTSP URL
<video id="test_video" controls autoplay src="rtsp://your_rtsp_stream/url"></video>
Setup player in your js:
import * as rtsp from 'rtsp_player';
rtsp.RTSP_CONFIG['websocket.url'] = "ws://websocket_proxy_address/ws"; // You should specify address of proxy described below
let player = rtsp.attach(document.getElementById('test_video'));
ES6 Modules support is required. You can use webpack with babel loader to build this script: webpack.config.js
const PATHS = {
src: {
test: path.join(__dirname, 'test.js')
},
dist: __dirname
};
module.exports = {
entry: PATHS.src,
output: {
path: PATHS.dist,
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
module: {
loaders: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel',
query: {
presets: ['es2015', 'stage-3', 'stage-2', 'stage-1', 'stage-0']
}
}
]
},
resolve: {
alias: {
rtsp: path.join(__dirname,'node_modules/html5_rtsp/src')
}
}
};
> npm install bp_event bp_log bp_statemachine > webpack --config webpack.config.js
Include compiled script into your HTML:
<script src="test.bundle.js"></script>
- Install websocket proxyFor Debian-based systems:
curl -o- http://repo.tom.ru/rpm/websockrtsprepo-1-0.deb | dpkg --install apt install websockrtspproxy # Debian-based systems
or Fedora:dnf install http://repo.tom.ru/rpm/websock_rtsp_repo-1-0.noarch.rpm dnf install websock_rtsp_proxy
- Configure port in /etc/ws_rtsp.ini This port should be open in your firewall. Also you can pass request to this port from your proxy. (for example: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/websocket.html)
- Run it
> service ws_rtsp start
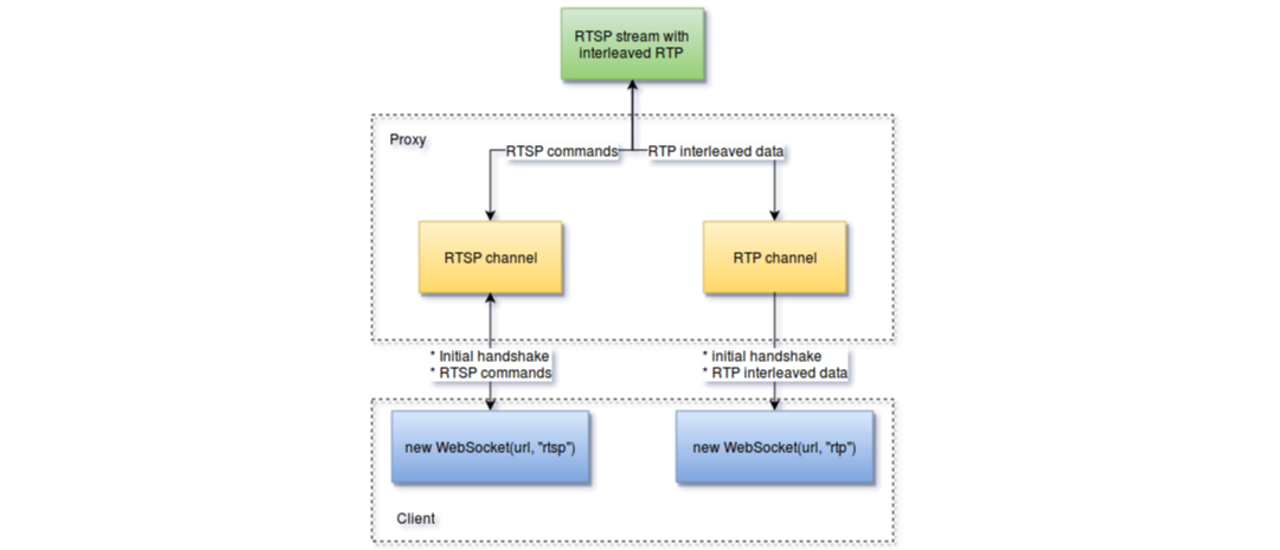
RTSP player establish connection with proxy with following protocol:
- Connect to RTSP channel by connecting websocket with "rtsp" protocol
specified and get connection id
c>s: WSP 1.0 INIT\r\n host <RTSP stream host>\r\n port <RTSP stream port>\r\n\r\n s>c: INIT <connection_id>\r\n\r\n conection_id = -1 means error
- Connect to RTP channel by connecting websocket with "rtp" protocol
c>s: WSP 1.0 INIT\r\n RTSP <connection_id achieved from RTSP socket initialization>\r\n\r\n s>c: INIT <connection_id>\r\n\r\n conection_id = -1 means error
- RTP channel should send interleaved data with 4 byte header ($<channel> <size>). Separate RTP is not supported at this moment
You can download this project on GitHub
Have any suggestions to improve our player? Feel free to leave comments or ideas